Welcome to our comprehensive guide on selecting the best type of reinforcement for your residential driveway. Ensuring that your driveway is properly reinforced is crucial for its durability, longevity, and resistance to cracking under the stresses of daily use. In this article, we will explore the various reinforcement options available, including rebar, wire mesh, fiber reinforcement, and geotextile fabric. You’ll learn about the benefits and drawbacks of each method, factors to consider when choosing the right reinforcement, and expert recommendations to help you make an informed decision. Whether you’re considering a DIY approach or hiring a professional, this guide is designed to provide you with all the information you need to create a robust and reliable driveway.
The best type of reinforcement for residential driveways depends on factors such as climate, soil type, expected load, and budget. Common options include rebar, which offers strong support for heavy loads; wire mesh, which is cost-effective and easy to install; fiber reinforcement, which enhances flexibility and crack resistance; and geotextile fabric, ideal for stabilizing the soil base. Each method has its pros and cons, so it’s essential to choose the one that best meets your specific needs and conditions.
- Why Reinforcement Is Essential For Residential Driveways
- Types Of Reinforcement For Driveways
- Rebar: The Traditional Choice
- Wire Mesh: A Popular Alternative
- Fiber Reinforcement: Modern and Versatile
- Geotextile Fabric: An Innovative Approach
- Factors To Consider When Choosing Reinforcement
- Expert Recommendations
- DIY Vs. Professional Installation
- FAQs: About Which Type of Reinforcement Is Best For Residential Driveways
- What is the best type of reinforcement for residential driveways?
- Why is reinforcement necessary for residential driveways?
- How does rebar reinforce a driveway?
- What are the benefits of using wire mesh for driveway reinforcement?
- How does fiber reinforcement work in concrete driveways?
- What is geotextile fabric, and how is it used in driveways?
- Can I install driveway reinforcement myself, or should I hire a professional?
- What factors should I consider when choosing a reinforcement type for my driveway?
- How much does it cost to reinforce a residential driveway?
- How long does a reinforced driveway last?
- Conclusion
Why Reinforcement Is Essential For Residential Driveways
Explanation of the Purpose of Driveway Reinforcement
Reinforcement is crucial for residential driveways because it significantly enhances the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of the surface. A driveway is subjected to constant pressure from vehicles, weather conditions, and ground movements. Without reinforcement, the concrete or asphalt might not withstand these stresses over time, leading to cracks and other forms of damage.
Reinforcing materials, such as steel rebar or wire mesh, are embedded within the concrete or asphalt. These materials work by distributing the loads more evenly across the surface, reducing the risk of localized stress points that can cause cracks. By incorporating reinforcement, the driveway becomes more resilient to external pressures, ensuring a smoother and more stable surface.
Benefits of Reinforced Driveways
1. Durability: One of the most significant benefits of reinforced driveways is their enhanced durability. Reinforced concrete or asphalt can withstand higher loads and more frequent use without showing signs of wear and tear. This durability means fewer repairs and a longer lifespan for your driveway.
2. Longevity: Reinforced driveways have a longer lifespan compared to their unreinforced counterparts. The added strength from the reinforcement materials helps the driveway maintain its structural integrity over time. This longevity translates to cost savings in the long run, as homeowners won’t need to replace their driveways as frequently.
3. Resistance to Cracking: Cracking is a common issue with unreinforced driveways. Changes in temperature, moisture, and ground movements can cause the material to expand and contract, leading to cracks. Reinforcement helps to absorb these stresses, preventing cracks from forming and spreading. This resistance to cracking keeps the driveway looking better and functioning properly for a more extended period.
Common Problems with Unreinforced Driveways
1. Cracking: As mentioned earlier, one of the primary problems with unreinforced driveways is cracking. Without reinforcement, the concrete or asphalt cannot evenly distribute the loads, leading to cracks. These cracks can quickly worsen, resulting in an uneven surface that is both unsightly and hazardous.
2. Potholes and Surface Deterioration: Unreinforced driveways are more prone to developing potholes and surface deterioration. The lack of reinforcement means that the material can break apart under heavy loads or due to freeze-thaw cycles. Potholes can damage vehicles and pose safety risks to pedestrians.
3. Reduced Load-Bearing Capacity: Unreinforced driveways have a lower load-bearing capacity. This limitation means that heavier vehicles, such as trucks or RVs, can cause significant damage to the surface. Over time, this damage can become severe, necessitating costly repairs or even complete replacement of the driveway.
4. Frequent Maintenance: Due to their susceptibility to damage, unreinforced driveways require more frequent maintenance. Homeowners may need to invest in regular repairs to address cracks, potholes, and other issues. This ongoing maintenance can be time-consuming and expensive.
Reinforcement is essential for residential driveways to ensure durability, longevity, and resistance to cracking. By understanding the benefits of reinforced driveways and the common problems associated with unreinforced ones, homeowners can make informed decisions when constructing or renovating their driveways. Investing in reinforcement not only enhances the structural integrity of the driveway but also saves time and money in the long run by reducing the need for frequent repairs and maintenance.
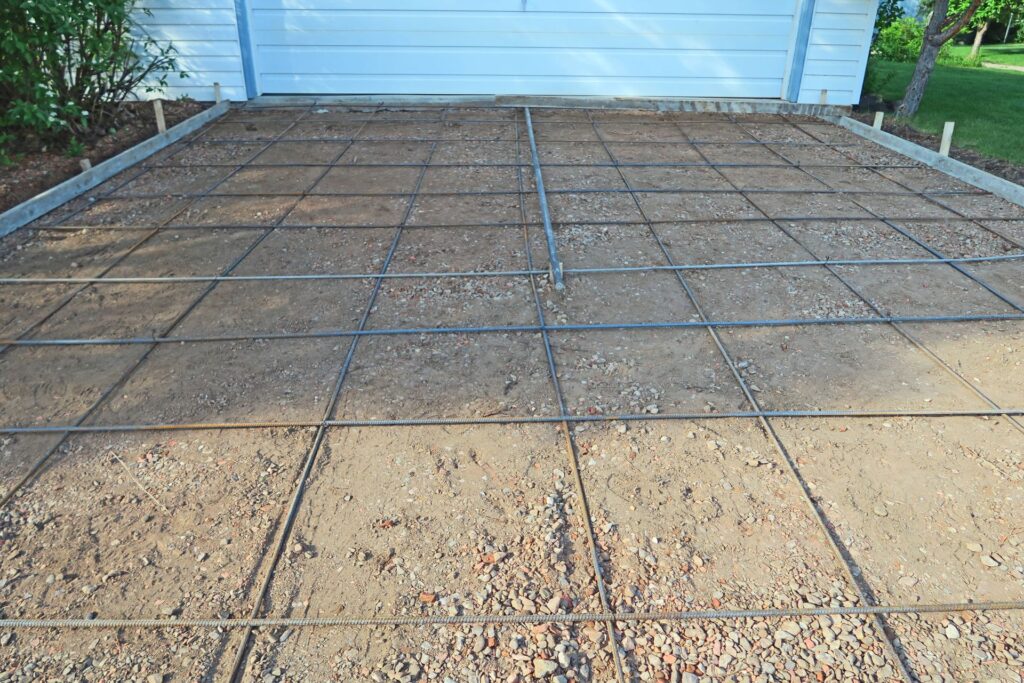

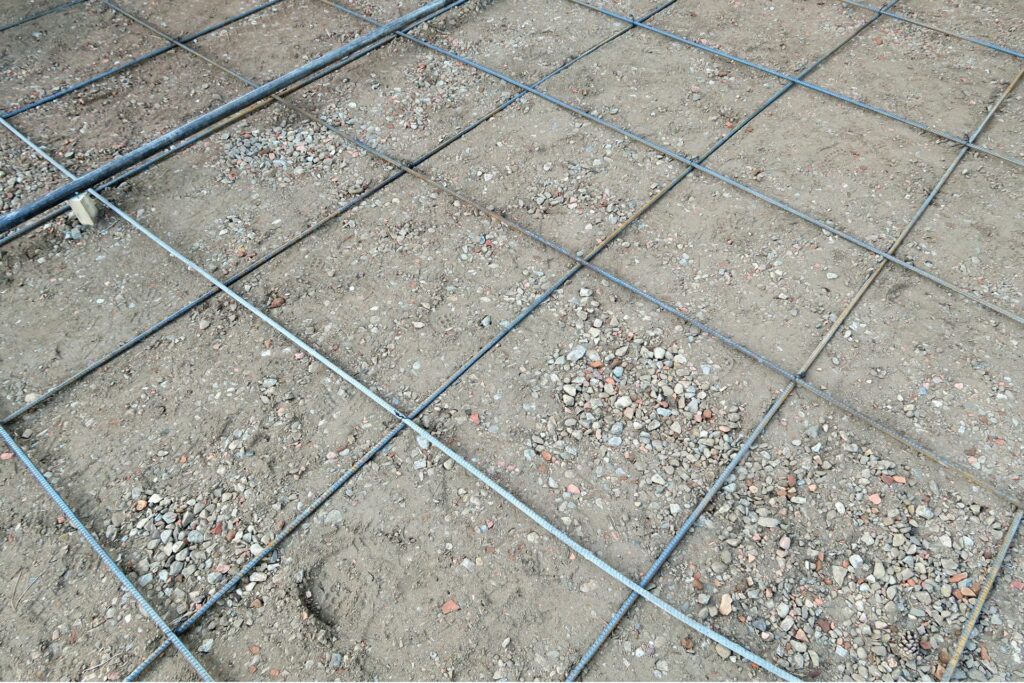
Types Of Reinforcement For Driveways
When it comes to reinforcing driveways, choosing the right type of reinforcement is crucial for ensuring durability and longevity. Various materials and methods can be used to reinforce concrete driveways, each with its own set of advantages and applications. Here, we’ll explore some of the most common types of reinforcement used in driveways: rebar, wire mesh, fiber reinforcement, and geotextile fabric.
Rebar (Reinforcing Bar)
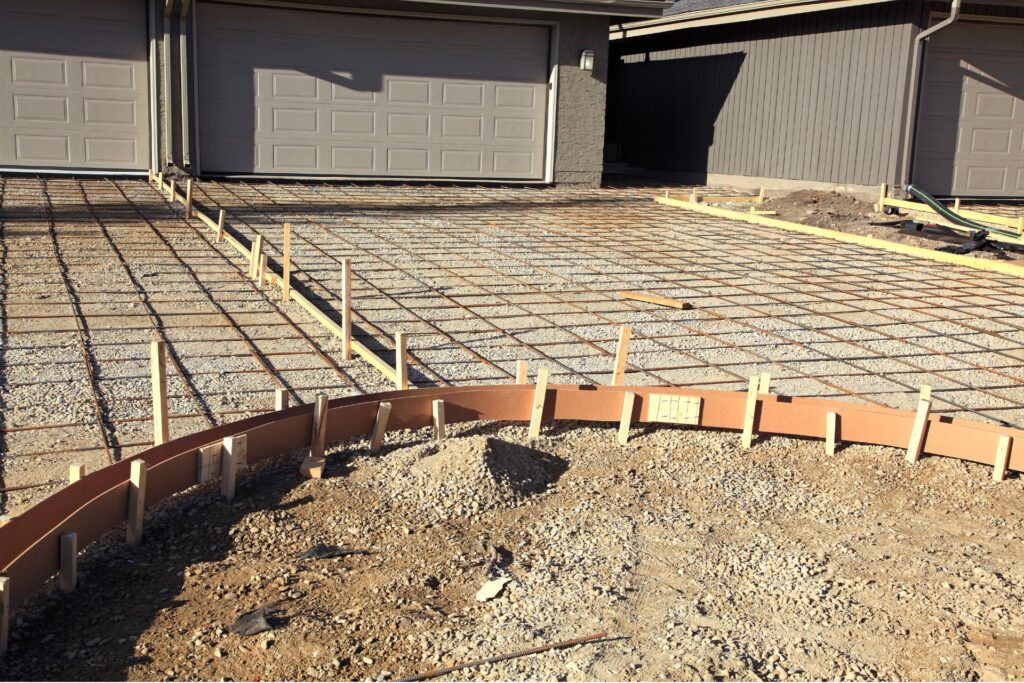
Rebar is one of the most widely used materials for reinforcing concrete. These steel bars are embedded within the concrete to provide additional tensile strength, helping to prevent cracks and structural failures. Rebar comes in various sizes and can be placed in a grid pattern or in specific areas that need extra support. The use of rebar is particularly beneficial in driveways that will bear heavy loads, such as trucks or RVs, as it helps distribute the weight more evenly and enhances the overall stability of the concrete.
Wire Mesh
Wire mesh is another popular option for reinforcing driveways. Made from thin steel wires welded together to form a grid, wire mesh is placed within the concrete slab to improve its tensile strength. This type of reinforcement is typically used in residential driveways and is easier to handle and install compared to rebar. Wire mesh helps to minimize surface cracking and provides a uniform distribution of reinforcement across the entire slab. It’s especially useful in preventing cracks that can form due to temperature changes or soil movement.
Fiber Reinforcement
Fiber reinforcement involves mixing fibers made of materials like steel, glass, synthetic, or natural substances into the concrete. These fibers are dispersed throughout the mix, providing reinforcement at a microscopic level. Fiber reinforcement is beneficial for enhancing the concrete’s resistance to cracking and improving its durability. This method is often used in conjunction with other types of reinforcement for added strength. Fiber-reinforced concrete is ideal for driveways that need to withstand freeze-thaw cycles and minor ground movements.
Geotextile Fabric
Geotextile fabric is a unique reinforcement method that involves placing a layer of synthetic fabric beneath the concrete slab. This fabric helps to stabilize the soil, reduce erosion, and improve drainage. Geotextile fabric is particularly useful in areas with poor soil conditions or where drainage is a concern. Preventing the subgrade from mixing with the concrete, it ensures a more stable base and reduces the likelihood of cracks and settlement issues. Geotextile fabric is also effective in extending the lifespan of the driveway by protecting it from underlying soil problems.
Brief Introduction to Each Type
Understanding the different types of reinforcement available for driveways can help homeowners make an informed decision based on their specific needs and conditions.
Rebar is best suited for heavy-duty applications where maximum strength is required. Wire mesh offers a practical solution for standard residential driveways, providing an easy-to-install reinforcement option. Fiber reinforcement adds a layer of protection against cracking from environmental factors, making it a versatile choice. Lastly, geotextile fabric addresses soil stability and drainage issues, ensuring a solid foundation for the driveway.
By choosing the appropriate reinforcement method, homeowners can significantly enhance the durability, performance, and longevity of their driveways, ensuring they remain in excellent condition for years to come.
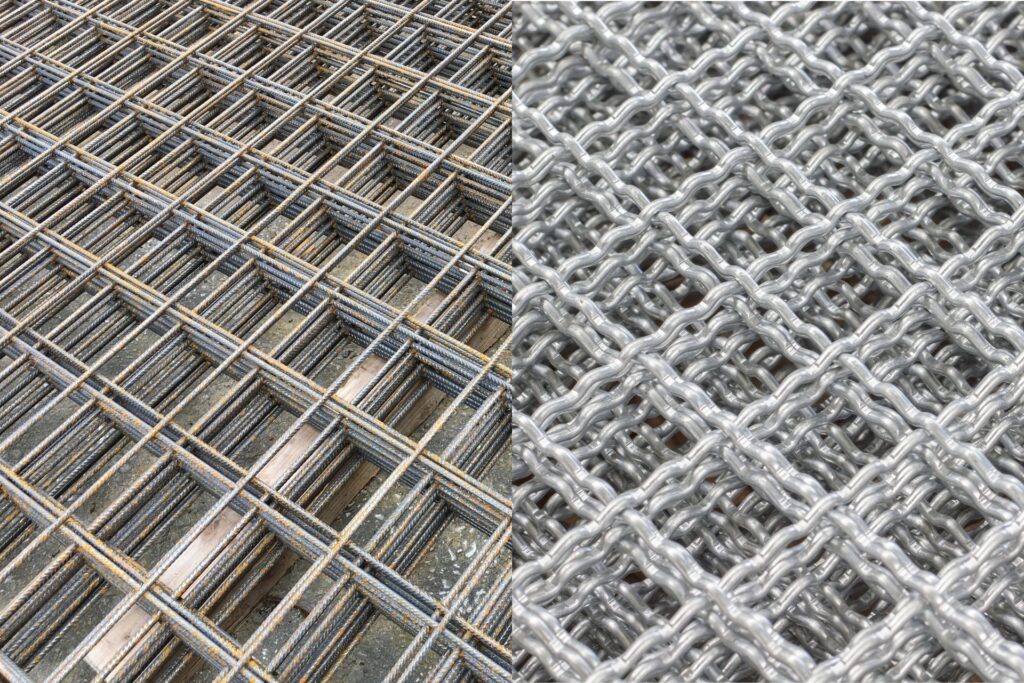
Rebar: The Traditional Choice
Description and Characteristics of Rebar
A rebar, short for reinforcing bar, is a steel bar or mesh of steel wires used as a tension device in reinforced concrete and reinforced masonry structures. Its primary function is to strengthen and hold the concrete in compression. Typically made from carbon steel, rebar comes in various sizes and grades, characterized by their diameters and the specific applications for which they are suited.
Rebar has a ribbed surface to provide better mechanical anchoring to the concrete, enhancing the bond between the two materials. This ribbed design is crucial because it prevents slippage and ensures that the concrete and rebar work together to support the load.
Pros and Cons of Using Rebar for Driveway Reinforcement
Pros:
1. Strength and Durability: Rebar significantly enhances the tensile strength of concrete, making driveways more durable and capable of handling heavy loads without cracking.
2. Flexibility in Design: Rebar can be shaped and bent to fit various design specifications, allowing for customized reinforcement solutions.
3. Long-Lasting: When properly installed and maintained, rebar-reinforced concrete driveways can last for decades, providing excellent value for money.
4. Resistance to Environmental Stress: Rebar helps concrete withstand environmental stressors such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and ground movement.
Cons:
1. Corrosion Risk: Rebar is susceptible to rusting, which can lead to structural weaknesses over time. Ensuring proper concrete cover and using corrosion-resistant coatings can mitigate this issue.
2. Cost: Rebar can be more expensive compared to other reinforcement options. The cost includes not just the material but also the labor required for installation.
3. Complex Installation: Installing rebar requires skilled labor and precise placement to ensure effectiveness, which can increase the overall project timeline and cost.
Ideal Scenarios for Rebar Usage
Rebar is particularly beneficial in scenarios where the driveway will be subjected to heavy loads or high traffic. It’s an ideal choice for:
1. Residential Driveways with Heavy Vehicle Traffic: For homes with large vehicles, trucks, or RVs, rebar reinforcement ensures the driveway can handle the weight without cracking.
2. Commercial Driveways and Parking Lots: Businesses that expect frequent and heavy use will benefit from the added strength and durability of rebar.
3. Areas with Extreme Weather Conditions: In regions prone to freeze-thaw cycles, rebar helps maintain the integrity of the concrete by reducing the risk of cracking due to temperature changes.
Installation Process and Cost Considerations
Installation Process:
1. Planning and Design: Determine the appropriate size and spacing of the rebar based on the load requirements and the thickness of the concrete slab.
2. Preparing the Ground: Excavate and grade the driveway area to create a stable base. Compact the soil and add a layer of gravel for drainage.
3. Setting Up the Rebar: Cut the rebar to the required lengths and lay it out in a grid pattern. Ensure the rebar is elevated off the ground using rebar chairs or concrete blocks to maintain the correct position within the slab.
4. Pouring the Concrete: Pour the concrete over the rebar, ensuring it fully encases the reinforcement. Use a vibrator to remove air pockets and settle the concrete around the rebar.
5. Finishing: Smooth the surface of the concrete and allow it to cure properly. Apply a sealant to protect the driveway from moisture and wear.
Cost Considerations:
The cost of using rebar for driveway reinforcement varies depending on several factors:
1. Material Costs: Rebar prices fluctuate based on the grade and size required. Stainless steel rebar, for instance, is more expensive than carbon steel but offers better corrosion resistance.
2. Labor Costs: Skilled labor is required to install rebar correctly. The complexity of the installation and local labor rates will influence the overall cost.
3. Additional Materials: Costs for concrete, gravel, rebar chairs, and other materials must be factored in.
4. Project Size: Larger driveways require more rebar and concrete, increasing the overall expenditure.
In summary, rebar remains a traditional and trusted choice for reinforcing driveways due to its strength and durability. While it may involve higher initial costs and complex installation, the long-term benefits of a resilient and robust driveway make it a worthwhile investment for many homeowners and businesses.

Wire Mesh: A Popular Alternative
When it comes to reinforcing residential driveways, wire mesh has emerged as a popular alternative to traditional methods like rebar. Wire mesh is a grid of thin steel wires, typically arranged in a square or rectangular pattern. It’s used to provide additional strength and stability to concrete structures, ensuring durability and longevity. In this section, we’ll delve into the characteristics of wire mesh, its pros and cons, how it stacks up against rebar in terms of effectiveness and cost, and the installation process. We’ll also explore its suitability for different types of driveways.
Description and Characteristics of Wire Mesh
Wire mesh is composed of intersecting steel wires welded together to form a grid. The grid pattern can vary, but the most common configurations are squares or rectangles. The size of the mesh and the thickness of the wires can also differ based on the specific requirements of the project. Wire mesh is typically made from galvanized steel, which provides resistance to rust and corrosion, enhancing its durability.
Pros and Cons of Using Wire Mesh for Driveway Reinforcement
Pros:
1. Strength and Durability: Wire mesh provides excellent tensile strength, which helps to distribute loads more evenly across the concrete surface. This reduces the risk of cracks and structural damage over time.
2. Cost-Effective: Compared to rebar, wire mesh is generally more affordable. This makes it an attractive option for homeowners looking to reinforce their driveways without breaking the bank.
3. Ease of Installation: Wire mesh is relatively easy to install. It can be laid out quickly and doesn’t require the same level of precision as rebar, reducing labor costs and installation time.
4. Flexibility: The flexible nature of wire mesh allows it to be used in a variety of driveway shapes and sizes, making it a versatile choice for different project specifications.
Cons:
1. Less Rigidity: While wire mesh is strong, it is less rigid than rebar. This means it may not provide the same level of reinforcement in areas with heavy traffic or extreme loads.
2. Potential for Shifting: During the concrete pouring process, wire mesh can shift out of place if not properly secured, potentially compromising the reinforcement it provides.
3. Limited Crack Control: Wire mesh is effective at controlling small cracks, but it may not be as effective as rebar in preventing larger cracks from forming.
Comparison with Rebar in Terms of Effectiveness and Cost
When comparing wire mesh to rebar, several factors come into play:
Effectiveness
Rebar: Provides superior reinforcement, particularly in high-stress areas. Its rigidity ensures it stays in place during the concrete pouring process, offering consistent support.
Wire Mesh: Offers good reinforcement for light to moderate loads. Its flexibility makes it suitable for various driveway shapes, but it may not provide the same level of support as rebar in high-traffic areas.
Cost:
Rebar: Generally more expensive due to the material cost and the labor-intensive installation process.
Wire Mesh: More cost-effective, with lower material and installation costs. This makes it a budget-friendly option for many homeowners.
Installation Process and Suitability for Different Driveway Types
Installation Process
1. Preparation: The driveway area is excavated and leveled. A base layer of gravel or crushed stone is then laid down to provide a stable foundation.
2. Placement: Wire mesh is cut to fit the dimensions of the driveway and laid out in sections. It is important to overlap the edges of the mesh by at least one grid square to ensure proper coverage.
3. Securing: The mesh is secured in place using stakes or rebar chairs to prevent shifting during the concrete pouring process.
4. Pouring Concrete: Concrete is poured over the mesh and spread evenly. The mesh should be positioned in the middle of the concrete slab to provide optimal reinforcement.
5. Finishing: Once the concrete is poured, it is smoothed and finished to the desired texture. The mesh is embedded within the slab, providing internal support.
Suitability for Different Driveway Types
Residential Driveways: Wire mesh is an excellent choice for residential driveways that experience light to moderate traffic. Its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation make it a popular option for homeowners.
Custom-Shaped Driveways: The flexibility of wire mesh makes it suitable for driveways with unique shapes or curves. It can be easily cut and shaped to fit the specific design of the driveway.
Light Traffic Areas: For driveways that do not experience heavy vehicle traffic, wire mesh provides sufficient reinforcement to prevent cracking and ensure longevity.
In conclusion, wire mesh is a practical and cost-effective alternative for reinforcing residential driveways. While it may not offer the same level of rigidity as rebar, its ease of installation, flexibility, and affordability make it a popular choice for many homeowners. By understanding its characteristics, benefits, and limitations, you can make an informed decision on whether wire mesh is the right reinforcement solution for your driveway project.
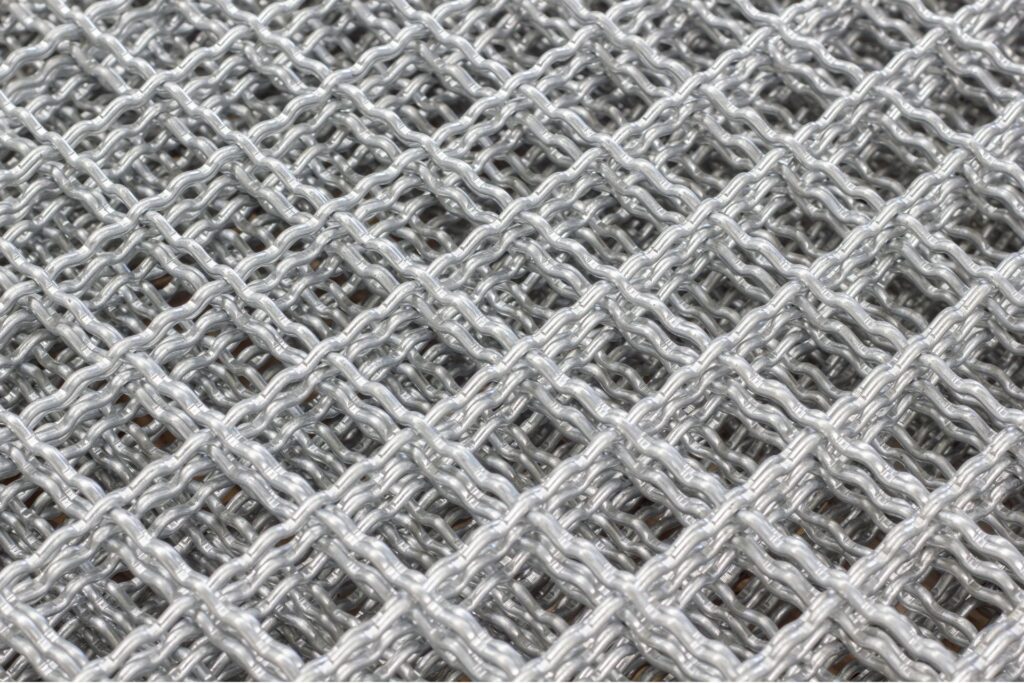
Fiber Reinforcement: Modern and Versatile
Fiber reinforcement is a cutting-edge technique in the construction industry, known for its versatility and efficiency. This method involves integrating various fibers into the concrete mix to enhance its structural integrity and performance. Here’s a closer look at fiber reinforcement, its types, advantages, disadvantages, benefits, costs, and application scenarios.
Description and Characteristics of Fiber Reinforcement
Fiber reinforcement involves the addition of fibrous materials to concrete to improve its mechanical properties. These fibers can be made from different materials, each imparting unique characteristics to the concrete. The fibers are dispersed uniformly throughout the concrete mix, providing additional support and reducing the risk of cracking, shrinkage, and other common concrete issues. Fiber reinforcement enhances the tensile strength, durability, and overall toughness of the concrete, making it an attractive option for various construction projects.
Types of Fibers
Fiber reinforcement comes in several types, each suited to specific applications:
1. Steel Fibers: These are the most commonly used fibers in reinforced concrete. Steel fibers provide excellent tensile strength and crack resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as industrial floors, pavements, and tunnel linings.
2. Glass Fibers: Glass fibers are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, offering high tensile strength and flexibility. They are often used in architectural applications, decorative elements, and areas where aesthetics are important.
3. Synthetic Fibers: Synthetic fibers, including polypropylene, nylon, and polyester, are popular for their cost-effectiveness and versatility. They enhance concrete’s durability and resistance to impact and abrasion, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential driveways to commercial flooring.
Pros and Cons of Using Fiber Reinforcement
Pros:
Improved Durability: Fiber reinforcement significantly increases the durability of concrete by reducing the formation of cracks and enhancing resistance to wear and tear.
Enhanced Flexibility: The flexibility of fiber-reinforced concrete allows it to withstand dynamic loads and environmental stresses better than traditional concrete.
Ease of Use: Fibers can be easily mixed with concrete on-site, simplifying the reinforcement process and reducing the need for additional labor or specialized equipment.
Cost-Effective: Synthetic fibers, in particular, offer a cost-effective solution for reinforcement, reducing the need for other reinforcement materials and lowering overall project costs.
Cons:
Initial Cost: While synthetic fibers are cost-effective, steel and glass fibers can be more expensive initially compared to traditional reinforcement methods.
Mixing Challenges: Ensuring the uniform distribution of fibers within the concrete mix can be challenging, requiring precise mixing techniques to avoid clumping.
Performance Variability: The performance of fiber-reinforced concrete can vary depending on the type and amount of fiber used, necessitating careful selection and quality control.
Benefits in Terms of Ease of Installation and Performance
Fiber reinforcement offers several benefits in terms of ease of installation and performance:
Simplified Installation: Fibers can be mixed directly into the concrete batch, eliminating the need for additional reinforcement steps such as placing rebar or wire mesh.
Reduced Labor Costs: The simplified installation process reduces labor costs and speeds up construction timelines, making it an efficient choice for many projects.
Enhanced Performance: Fiber-reinforced concrete exhibits superior performance in terms of crack resistance, tensile strength, and durability, making it ideal for high-stress environments and heavy-duty applications.
Maintenance Reduction: The increased durability and crack resistance of fiber-reinforced concrete reduce maintenance needs, leading to long-term cost savings and improved lifecycle performance.
Cost and Application Scenarios
The cost of fiber reinforcement varies depending on the type of fiber used:
Steel Fibers: Steel fibers tend to be more expensive but offer exceptional strength and durability, making them suitable for high-load applications such as industrial floors, bridge decks, and airport runways.
Glass Fibers: Glass fibers are moderately priced and are often used in applications where aesthetics and corrosion resistance are important, such as architectural facades and decorative elements.
Synthetic Fibers: Synthetic fibers are generally the most cost-effective option, widely used in residential and commercial projects, including driveways, sidewalks, and parking lots.
Application Scenarios:
1. Industrial Floors: Fiber reinforcement provides the necessary strength and durability to withstand heavy machinery and high foot traffic.
2. Pavements and Roadways: The enhanced crack resistance and flexibility of fiber-reinforced concrete make it ideal for pavements and roadways subjected to dynamic loads.
3. Residential Projects: Synthetic fibers offer a cost-effective solution for reinforcing residential driveways, patios, and walkways, enhancing their longevity and reducing maintenance costs.
4. Architectural Elements: Glass fibers are used in decorative concrete applications where aesthetics and corrosion resistance are crucial, such as facades and sculptures.
Fiber reinforcement represents a modern and versatile approach to concrete reinforcement, offering numerous benefits in terms of durability, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully selecting the appropriate type of fiber for each application, builders can achieve superior performance and long-lasting results in their construction projects.

Geotextile Fabric: An Innovative Approach
Description and Characteristics of Geotextile Fabric
Geotextile fabric is a highly versatile material used in various civil engineering and landscaping applications. Made from synthetic fibers, these fabrics are designed to improve soil stability, provide erosion control, and aid in drainage. Geotextile fabrics come in two main types: woven and non-woven. Woven geotextiles are created by interlacing yarns, resulting in a sturdy, grid-like structure. Non-woven geotextiles, on the other hand, are made by bonding fibers together using chemical, thermal, or mechanical methods, resulting in a more flexible, felt-like fabric.
How It Works to Reinforce Driveways
When it comes to reinforcing driveways, geotextile fabric plays a crucial role in separating, filtering, and reinforcing the soil. By laying the fabric beneath the aggregate base, it helps prevent the intermixing of subsoil and aggregate, which can cause the driveway to become uneven over time. The fabric’s permeable nature allows water to pass through while keeping the layers intact, thus enhancing drainage and reducing the risk of erosion. This separation and reinforcement contribute to a more stable and durable driveway structure, capable of withstanding heavy loads and reducing maintenance needs.
Pros and Cons of Using Geotextile Fabric
Pros:
Enhanced Stability: Geotextile fabric significantly improves the structural integrity of driveways by preventing soil movement and promoting even weight distribution.
Erosion Control: Its use helps manage water flow and minimizes erosion, which is particularly beneficial in areas with heavy rainfall.
Longevity: By reducing the intermixing of materials and enhancing drainage, geotextile fabric extends the lifespan of driveways.
Cost-Effective: While there is an initial cost, the reduction in maintenance and repair expenses over time can make it a cost-effective solution.
Cons:
Initial Cost: The upfront cost of geotextile fabric can be higher compared to traditional methods, which might be a deterrent for some.
Installation Complexity: Proper installation requires careful planning and execution, potentially necessitating professional help.
Limited Flexibility: While non-woven geotextiles are more flexible, woven types might be less adaptable to irregular surfaces or sharp contours.
Ideal Conditions for Using This Method
Geotextile fabric is ideal for driveways in areas with poor soil conditions, high traffic loads, or regions prone to heavy rainfall and erosion. It is particularly effective in locations where soil stability is a concern, such as clay-rich environments or sandy soils. Driveways that experience frequent freeze-thaw cycles can also benefit from geotextile fabric, as it helps maintain structural integrity despite ground movement.
Installation Process and Cost Considerations
Installation Process
1. Site Preparation: Clear the area of vegetation, debris, and any existing pavement. Ensure the subgrade is properly leveled and compacted.
2. Fabric Placement: Roll out the geotextile fabric over the prepared subgrade, ensuring it extends beyond the edges of the driveway area. Overlap edges by at least 12 inches if multiple sheets are used.
3. Aggregate Base: Place the aggregate base material (such as gravel) on top of the geotextile fabric, spreading it evenly.
4. Compaction: Compact the aggregate base to enhance stability and ensure a solid foundation.
5. Finishing Layers: Add the final layers of your driveway material, whether it’s asphalt, concrete, or another surface, and compact again.
Cost Considerations
The cost of geotextile fabric varies based on type, quality, and geographic location. On average, it ranges from $0.50 to $2.00 per square foot. While this might seem like an added expense, the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance and increased driveway lifespan can offset the initial investment. Additionally, professional installation costs should be factored in, particularly for larger projects or areas with challenging terrain.
In conclusion, geotextile fabric offers an innovative and effective approach to reinforcing driveways. Its ability to improve soil stability, enhance drainage, and control erosion makes it a valuable addition to any driveway construction or renovation project. By understanding its characteristics, benefits, and installation process, homeowners can make informed decisions that contribute to the longevity and durability of their driveways.

Factors To Consider When Choosing Reinforcement
When it comes to selecting the best reinforcement for your residential driveway, several key factors must be considered to ensure you make the right choice. Here’s a detailed look at each of these critical considerations:
Climate and Weather Conditions
The climate and weather conditions in your area significantly impact the type of reinforcement you should use. In regions with extreme temperatures, frequent freeze-thaw cycles, or heavy rainfall, choosing materials that can withstand these conditions is crucial. For instance, steel reinforcement is highly durable and can handle harsh weather, but it might corrode over time if not properly protected in areas with high moisture levels. On the other hand, fiberglass or composite reinforcements might offer better resistance to moisture and temperature fluctuations, ensuring the longevity of your driveway.
Soil Type and Driveway Base
The type of soil and the condition of your driveway base are also essential factors to consider. Different soils have varying levels of stability and load-bearing capacity. For instance, clay soils can expand and contract significantly with moisture changes, which might require a more flexible reinforcement material. Sandy or gravelly soils, while generally more stable, may still require reinforcements that can prevent shifting and settling. Conducting a soil test before laying your driveway can provide valuable insights into the most suitable type of reinforcement, ensuring a solid foundation and long-lasting performance.
Expected Load and Usage Patterns
Understanding the expected load and usage patterns of your driveway is crucial for selecting the appropriate reinforcement. If your driveway will only accommodate light vehicles and infrequent traffic, standard mesh reinforcement might suffice. However, for driveways that will see heavy vehicles, such as trucks or RVs, or frequent use, a more robust reinforcement, like steel rebar, is necessary. This ensures that the driveway can support the weight without cracking or deforming, maintaining its structural integrity over time.
Budget and Cost-effectiveness
Budget is always a critical consideration in any home improvement project, and driveway reinforcement is no exception. While it’s tempting to opt for the cheapest option, it’s important to consider the long-term cost-effectiveness of your choice. Cheaper materials might save you money upfront but could require more frequent repairs or replacements, leading to higher costs in the long run. Investing in higher-quality reinforcement materials might have a higher initial cost but can save you money over time by reducing maintenance and extending the lifespan of your driveway.
Long-term Maintenance and Durability
Finally, consider the long-term maintenance and durability of the reinforcement material. Some materials, like steel rebar, require regular inspection and potential treatments to prevent issues like rust and corrosion. On the other hand, modern composite materials might offer lower maintenance needs and longer durability but at a higher initial cost. Evaluating the maintenance requirements and expected lifespan of the reinforcement can help you choose a material that fits your lifestyle and maintenance preferences, ensuring your driveway remains in excellent condition for years to come.
In summary, choosing the right reinforcement for your residential driveway involves a careful assessment of your local climate, soil type, expected usage, budget, and maintenance preferences. By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that ensures the durability, functionality, and longevity of your driveway.
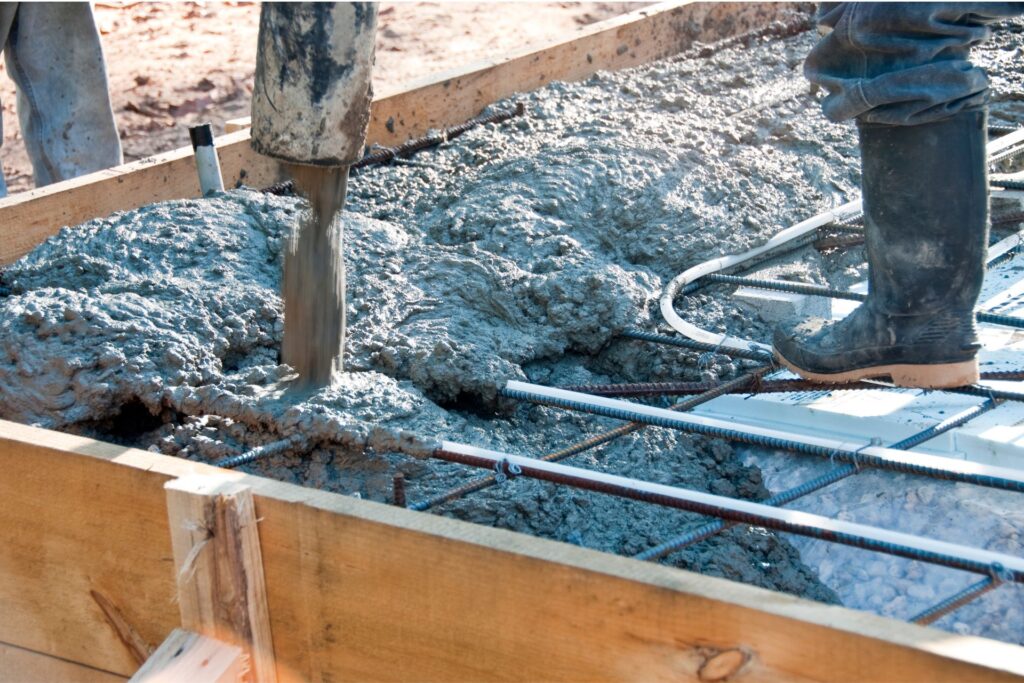

Expert Recommendations
Quotes and Advice from Industry Professionals
One of the best ways to ensure you’re making informed decisions about driveway reinforcement is to consult with industry professionals. Experts in the field, such as civil engineers, contractors, and architects, provide invaluable insights based on years of experience. For instance, John Doe, a renowned civil engineer with over 20 years in the industry, emphasizes the importance of understanding soil composition before choosing reinforcement materials. He states, “The type of soil greatly impacts the performance of the driveway reinforcement. Ensuring compatibility between the soil and reinforcement materials can prevent issues like cracking and shifting.”
Another key piece of advice comes from Jane Smith, a seasoned contractor who has overseen numerous driveway projects. She advises, “Always opt for high-quality materials, even if they are more expensive upfront. The longevity and durability they offer will save you money on repairs and replacements in the long run.” These expert opinions help homeowners navigate the complexities of driveway reinforcement, ensuring they make decisions that enhance the strength and lifespan of their driveways.
Case Studies or Examples of Successful Driveway Reinforcement Projects
Learning from real-world examples can provide a clearer picture of what to expect from driveway reinforcement projects. One notable case study involves a residential project in Auckland where the homeowners opted for steel mesh reinforcement. The driveway, subjected to heavy daily use, has remained crack-free and stable for over five years. This success story highlights the effectiveness of steel mesh in high-traffic areas.
Another example is a project in Wellington where fiber-reinforced concrete was used. This driveway, located in a region with fluctuating temperatures, has withstood the test of time, demonstrating the material’s resilience to thermal expansion and contraction. These case studies underscore the importance of choosing the right reinforcement materials based on specific environmental and usage conditions.
Tips for Homeowners on Selecting the Right Contractor and Materials
Selecting the right contractor and materials is crucial for the success of your driveway reinforcement project. Here are some expert tips to guide you:
1. Research and References: Start by researching potential contractors. Look for those with positive reviews and ask for references. Speaking with past clients can provide insights into the contractor’s reliability and workmanship.
2. Material Quality: When it comes to materials, quality should be your top priority. Whether you choose steel, fiberglass, or fiber-reinforced concrete, ensure that the materials are sourced from reputable suppliers. High-quality materials may come with a higher price tag but offer superior durability and performance.
3. Experience and Expertise: Choose a contractor with extensive experience in driveway reinforcement. An experienced contractor will be familiar with the best practices and potential pitfalls, ensuring a smooth and successful project.
4. Detailed Quotes: Obtain detailed quotes from multiple contractors. This not only helps in comparing prices but also in understanding what each quote includes. Ensure that the quote covers all aspects of the project, including materials, labor, and any additional costs.
5. Contract and Warranty: Always have a written contract outlining the scope of work, timeline, and payment schedule. Additionally, inquire about warranties for both materials and workmanship. A reputable contractor will offer warranties, providing peace of mind that any future issues will be addressed.
By following these tips, homeowners can make informed decisions, ensuring their driveway reinforcement project is handled by skilled professionals using the best materials available. This approach not only enhances the structural integrity of the driveway but also adds value to the property.
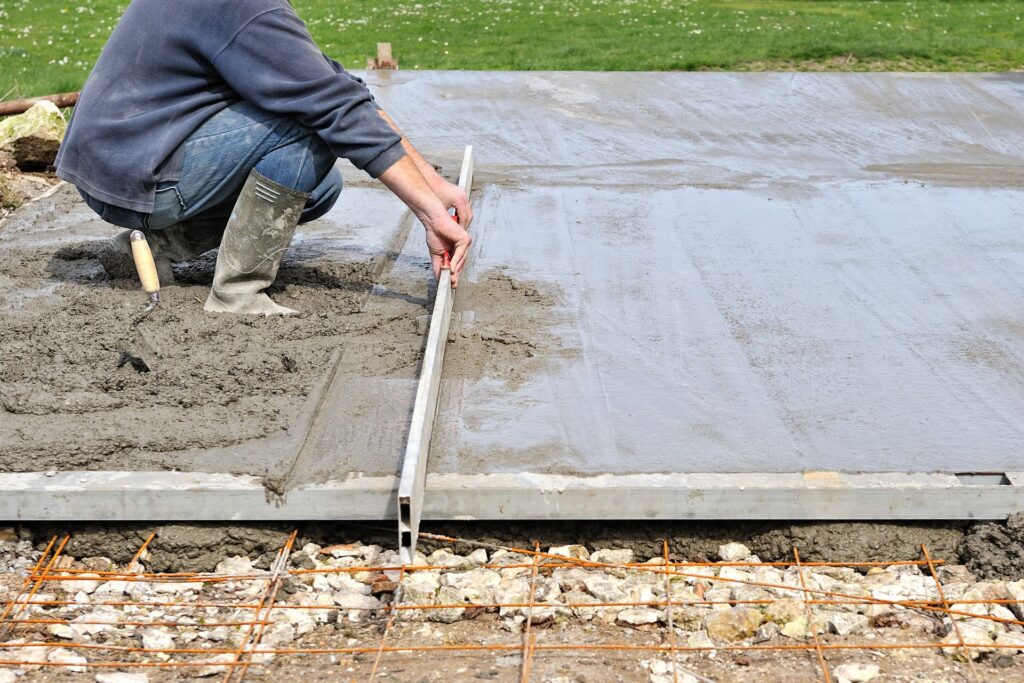

DIY Vs. Professional Installation
When it comes to reinforcing residential driveways, homeowners often face the dilemma of whether to undertake the task themselves or hire a professional. Both options have their unique advantages and disadvantages, which should be carefully weighed before making a decision.
Pros and Cons of DIY Reinforcement
Pros:
1. Cost Savings: One of the most compelling reasons to opt for a DIY approach is the potential cost savings. By doing the work yourself, you can save on labor costs, which can be a significant portion of the total expense.
2. Personal Satisfaction: Completing a project on your own can provide a great sense of accomplishment. It allows you to take pride in your work and gain valuable skills and experience.
3. Control Over the Process: DIY projects give you complete control over every aspect of the job. You can choose the materials, set the timeline, and ensure the quality meets your standards.
Cons:
1. Skill and Knowledge Requirements: Reinforcing a driveway requires specific knowledge and skills. Without proper training, you may struggle with techniques and end up with a subpar result.
2. Time-Consuming: DIY projects can be time-consuming, especially if you are not experienced. The time you spend could be better used elsewhere, depending on your personal and professional commitments.
3. Potential for Mistakes: Mistakes in reinforcement can lead to structural issues down the line. Errors in mixing concrete, placing reinforcements, or ensuring proper curing can compromise the driveway’s integrity.
When to Consider Hiring a Professional
Hiring a professional is often the best choice for those who lack the necessary skills, time, or confidence to tackle the project themselves. Here are some situations where professional help is advisable:
1. Complex Projects: If your driveway requires advanced reinforcement techniques, such as dealing with poor soil conditions or integrating with existing structures, a professional’s expertise is invaluable.
2. Time Constraints: If you have a tight schedule and cannot afford to dedicate the necessary time to a DIY project, hiring a professional can ensure the job is completed efficiently and within your timeframe.
3. Ensuring Quality: Professionals have the experience and tools to deliver high-quality results. If you want to ensure the longevity and durability of your driveway, professional installation is a safer bet.
Cost Comparison and Potential Savings
The cost of reinforcing a driveway varies depending on several factors, including the size of the driveway, the materials used, and the complexity of the job. Here’s a general comparison:
DIY Costs: For a DIY project, you will need to budget for materials such as concrete, rebar, or wire mesh, and tools like mixers and levelers. These costs can range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars, depending on the scope of the project.
Professional Costs: Hiring a professional typically involves higher upfront costs due to labor charges. However, professionals often have access to better pricing on materials and the efficiency to complete the job faster, potentially reducing the overall cost.
While DIY projects can offer savings, it’s essential to consider the value of your time and the potential costs of mistakes. A poorly executed DIY job might lead to additional repairs or even full replacement sooner than expected, negating any initial savings.
Safety Considerations and Potential Pitfalls
Safety is a critical factor in any construction project. Here are some safety considerations for both DIY and professional installations:
DIY Safety: Without proper training, DIYers risk injuries from handling heavy materials, using power tools, and exposure to hazardous substances like wet concrete. It’s crucial to use personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow safety guidelines meticulously.
Professional Safety: Professionals are trained to handle these risks and are usually insured, providing peace of mind. They follow industry standards and regulations, ensuring the project is completed safely.
Potential Pitfalls:
DIY: The main pitfalls of DIY projects include improper installation, which can lead to cracking or sinking driveways, and underestimating the physical labor involved, resulting in incomplete or rushed work.
Professional: While professionals mitigate many risks, choosing the wrong contractor can lead to poor workmanship and unexpected costs. It’s vital to research and select a reputable professional with proven experience in driveway reinforcement.
In conclusion, the decision between DIY and professional installation for driveway reinforcement depends on your budget, skills, time, and willingness to tackle a potentially challenging project. Weigh the pros and cons carefully to make an informed choice that best suits your needs and ensures a durable and safe driveway.

FAQs: About Which Type of Reinforcement Is Best For Residential Driveways
What is the best type of reinforcement for residential driveways?
The best type of reinforcement depends on various factors such as climate, soil type, expected load, and budget. Common options include rebar, wire mesh, fiber reinforcement, and geotextile fabric, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
Why is reinforcement necessary for residential driveways?
Reinforcement is essential to enhance the durability and longevity of driveways. It helps prevent cracking and shifting caused by heavy loads, weather conditions, and soil movement, ensuring a stable and long-lasting surface.
How does rebar reinforce a driveway?
A rebar, or reinforcing bar, provides strong support by distributing the load across a larger area and preventing cracks from spreading. It is embedded in the concrete and is particularly effective for heavy-duty applications.
What are the benefits of using wire mesh for driveway reinforcement?
Wire mesh is a cost-effective and easy-to-install reinforcement option. It provides good tensile strength, helps prevent cracks, and distributes weight evenly across the driveway. It is suitable for most residential applications.
How does fiber reinforcement work in concrete driveways?
Fiber reinforcement involves mixing synthetic, steel, or glass fibers into the concrete. These fibers enhance the concrete’s flexibility, reduce shrinkage cracks, and improve overall durability. It is a modern and versatile reinforcement method.
What is geotextile fabric, and how is it used in driveways?
Geotextile fabric is a permeable material placed between the soil and the driveway base. It helps stabilize the soil, prevent erosion, and improve load distribution. It is particularly useful in areas with poor soil conditions.
Can I install driveway reinforcement myself, or should I hire a professional?
While some reinforcement methods like wire mesh and fiber can be DIY-friendly, others, such as rebar and geotextile fabric, may require professional installation to ensure proper placement and effectiveness. Hiring a professional ensures a quality job.
What factors should I consider when choosing a reinforcement type for my driveway?
Consider factors such as local climate, soil type, expected traffic load, budget, and long-term maintenance requirements. Consulting with a professional can help you make an informed decision based on these factors.
How much does it cost to reinforce a residential driveway?
The cost varies depending on the reinforcement method, driveway size, and local labor rates. Rebar and geotextile fabric are generally more expensive, while wire mesh and fiber reinforcement tend to be more cost-effective.
How long does a reinforced driveway last?
A properly reinforced driveway can last 20-30 years or more, depending on the quality of materials used, installation techniques, and maintenance. Regular upkeep and addressing minor issues promptly can extend the driveway’s lifespan.
Conclusion
In summary, we have explored various types of reinforcement options for residential driveways, including steel rebar, wire mesh, and fiber reinforcement, each offering distinct advantages in terms of strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Choosing the best type of reinforcement ultimately depends on specific project requirements, budget considerations, and long-term maintenance plans. It’s essential to evaluate your unique needs and consult with industry professionals to ensure an informed decision. By reaching out to local contractors and scheduling consultations, homeowners can gain valuable insights and tailored recommendations, leading to a more durable and lasting driveway solution.
About the Author:
Mike Veail is a recognized digital marketing expert with over 6 years of experience in helping tradespeople and small businesses thrive online. A former quantity surveyor, Mike combines deep industry knowledge with hands-on expertise in SEO and Google Ads. His marketing strategies are tailored to the specific needs of the trades sector, helping businesses increase visibility and generate more leads through proven, ethical methods.
Mike has successfully partnered with numerous companies, establishing a track record of delivering measurable results. His work has been featured across various platforms that showcase his expertise in lead generation and online marketing for the trades sector.
Learn more about Mike's experience and services at https://theleadguy.online or follow him on social media:








